This site contains product affiliate links. We may receive a commission if you make a purchase after clicking on one of these links.
There’s no question that our body needs magnesium in order to function properly. It’s a co-factor in over 300 enzyme systems that regulate a variety of biochemical reactions in our bodies, so you could say it is a vital mineral for our health. (1)
The Role of Magnesium in the Body
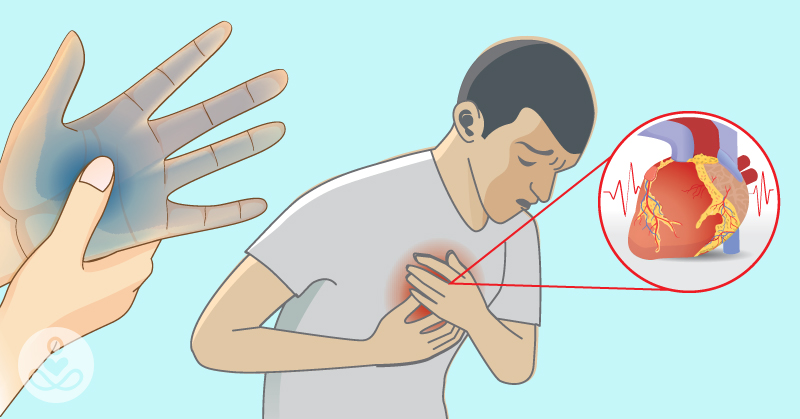
Without magnesium, our bodies would cease to function. The mineral is involved in the processes of nearly every nerve and muscle in your body. Without it, we wouldn’t be able to control our muscles, including the ever-important, life-giving muscle that is our heart. Without magnesium, none of these processes would occur, so you can imagine what havoc low levels of magnesium can have on your body and overall health. (1)
Read More: Should Vitamin D and Magnesium Be Taken Together?
The role of magnesium in the body includes:
- Protein synthesis
- Energy production (especially in oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis)
- Structural development of bones
- Synthesis (aka production) of DNA, RNA, and the antioxidant Glutathione
- Active transport of calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes: This is critical for muscle contractions, regular heart rhythms, and nerve impulse conduction
- Blood glucose control
- Blood pressure regulation
EarlyMagnesium Deficiency Symptoms include:

- fatigue
- weakness
- loss of appetite
- nausea and vomiting
- diarrhea
- nausea
- dizziness
As deficiency continues and becomes more severe, symptoms can include:
- abnormal heart rhythms and coronary spasms
- muscles twitch, spasms, or cramps
- numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness
- low blood pressure
- personality changes
- seizures
Mineral Imbalances

Extremely severe magnesium deficiency disrupts our body’s mineral balance and can cause hypocalcemia (low serum calcium) and hypokalemia (low serum potassium). (1) We love New Roots Herbal Pure Magnesium Bisglycinate Each plant-sourced capsule contains 130 mg of elemental magnesium in the form of highly bioavailable magnesium bisglycinate for maximum assimilation and minimal stomach upset. The pure form of magnesium bisglycinate is easily absorbed within the intestines. It’s also gentle on the stomach, and less likely to cause nausea and diarrhea which are more common with other forms of magnesium. Get your 60 day supply at The Health Shop for $34.78 while supplies last!
Read More: Natural Homemade Magnesium “Chill Pill” Gummies Great For Insomnia, Anxiety, And Stress
Why do people become Magnesium deficient?

Magnesium was primarily found in the topsoil and hence found its way into our food. New and modern farming techniques and the use of chemicals and fertilizers has rendered the soil devoid of magnesium. (1) In addition to the population’s habitually low dietary magnesium intake, excessive losses and inability to properly absorb the mineral are also caused by a few things such as GI disorders (Crohn’s Disease, Celiac’s Disease, regional enteritis, leaky gut). Those with Type II Diabetes and insulin resistance. Alcoholism and alcohol dependence, and aging.
The standard American diet is a primary cause for low magnesium levels in the population

Most of us eat too many overly processed foods filled with chemicals, preservatives, and additives that destroy our digestive systems, and not enough vegetables or other whole foods. On top of that, the vegetables, fruits, and whole food products that we are eating are harvested long before they are ready, sprayed with chemicals and pesticides, and shipped from thousands of miles away, leaving them much lower in nutritional value than the locally grown foods that used to make up the majority of our diets. (1)
Long-term Effects of Magnesium Deficiency

There are some pretty scary health problems that are correlated with the magnesium in our bodies. It’s not a surprise that these diseases, which are on the rise in North America, correlate with a decrease in the nutritional value of our food, and therefore a decrease in magnesium intake and absorption, as mentioned above. (1)
We love New Roots Herbal Pure Magnesium Bisglycinate Each plant-sourced capsule contains 130 mg of elemental magnesium in the form of highly bioavailable magnesium bisglycinate for maximum assimilation and minimal stomach upset. The pure form of magnesium bisglycinate is easily absorbed within the intestines. It’s also gentle on the stomach, and less likely to cause nausea and diarrhea which are more common with other forms of magnesium. Get your 60 day supply at The Health Shop for $34.78 while supplies last!
Read More: 15 Signs You Have a Magnesium Deficiency & The Foods You Need to Eat
1. Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease
Magnesium’s role in heart rhythms and blood pressure control put it right in line with CVD. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities assessed risk factors for heart disease and serum magnesium levels in over 14,000 African American and Caucasian women and men, aged 45 to 64, and then conducted a follow-up after 12 years. They found that those with the highest serum magnesium levels had a 38% reduced risk of heart attack than those with the lowest. (1, 2) This is just one of many studies done on the link between heart disease and magnesium, all which concluded that proper intakes of magnesium may reduce your risk of hypertension, stroke, and hear disease. (1, 2)
2. Type 2 Diabetes

Magnesium has a critical role in the metabolism and regulation of glucose, meaning that low levels of the mineral can cause insulin resistance, the precursor to this rampant disease. To make matters worse, Diabetes causes increased losses of magnesium through urine. This not only exacerbates the deficiency, but also effects the secretion and function of insulin in the body making Diabetes harder to control. (1, 3) Several studies have been done that show the connection between magnesium deficiency and type two Diabetes. However, there is currently still inconsistent evidence that supplementing with magnesium will improve Diabetes control for those who already have the disease. (1, 3)
3. Osteoporosis

Magnesium is not only important for the formation and building of bones, but it also has an effect on osteoclasts and osteoblasts (involved in bone formation and healing), concentrations of parathyroid hormone (for bone rebuilding/repair), and the concentrations of the active form of vitamin D. All of that means that magnesium has a hand involved with bone mineral density, and when that is low, we are at increased risk of developing Osteoporosis. (1, 4) In short: Low magnesium = low bone mineral density = high risk for Osteoporosis.
4. Migraines

Headache-promoting factors such as vasoconstriction (the constriction of blood vessels) and the release of neurotransmitter are closely tied to magnesium. Research has found that people who experience migraines have low serum and tissue levels of magnesium. Currently, however, there needs to be more research done on the effectiveness of magnesium supplementation and migraine prevention. (1, 5)
We love New Roots Herbal Pure Magnesium Bisglycinate Each plant-sourced capsule contains 130 mg of elemental magnesium in the form of highly bioavailable magnesium bisglycinate for maximum assimilation and minimal stomach upset. The pure form of magnesium bisglycinate is easily absorbed within the intestines. It’s also gentle on the stomach, and less likely to cause nausea and diarrhea which are more common with other forms of magnesium. Get your 60 day supply at The Health Shop for $34.78 while supplies last!
Read More: 5 Drinks That Effect How Well Your Body Absorbs Calcium and Magnesium
Testing for Magnesium Deficiency

Magnesium deficiency symptoms, like most deficiencies, are non-specific and could signal any number of nutrient deficiencies and health problems. If you have some of the symptoms mentioned above, how do you know if you are deficient? Unfortunately, there is no real reliable test to determine magnesium levels in the body. Most often, a blood test is taken, however considering 50-60% of the body’s magnesium is stored in our bones, serum levels don’t provide a true picture of total body or specific tissue levels. (1)
Other tests include:

- Measuring magnesium concentrations in erythrocytes, urine, and saliva
- Measuring Ionized concentrations in the blood, serum, and plasma
- Magnesium-loading or tolerance test: Clinically, this involves parenteral infusion of a large dose of magnesium and testing urinary outputs.
- Magnesium Stool test: Involves testing the amount of magnesium in your stool. This test is for diagnostic purposes only and is not approved for use in all states. (1, 6)
Due to the typical North American diet and the way our food system works

Chances are you are not reaching adequate intake levels of magnesium each day. While supplementing can have its place, especially for highly active individuals and anyone suffering from previously mentioned ailments, using pure magnesium oil and increasing the amount of magnesium-rich foods is a safe, natural way to boost your levels.
Foods High in Magnesium

There are so many magnesium-rich foods that you can include in your diet every day. Green leafy vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains the most magnesium-containing foods. (1, 7) Do you best to buy local and organic whenever possible, as these foods will not only have higher amounts of magnesium, but other vitamins and minerals as well, without the added toxins and chemicals that take away from the nutrient value of our food. (1, 7)
We love New Roots Herbal Pure Magnesium Bisglycinate Each plant-sourced capsule contains 130 mg of elemental magnesium in the form of highly bioavailable magnesium bisglycinate for maximum assimilation and minimal stomach upset. The pure form of magnesium bisglycinate is easily absorbed within the intestines. It’s also gentle on the stomach, and less likely to cause nausea and diarrhea which are more common with other forms of magnesium. Get your 60 day supply at The Health Shop for $34.78 while supplies last!
Foods with the Most Magnesium
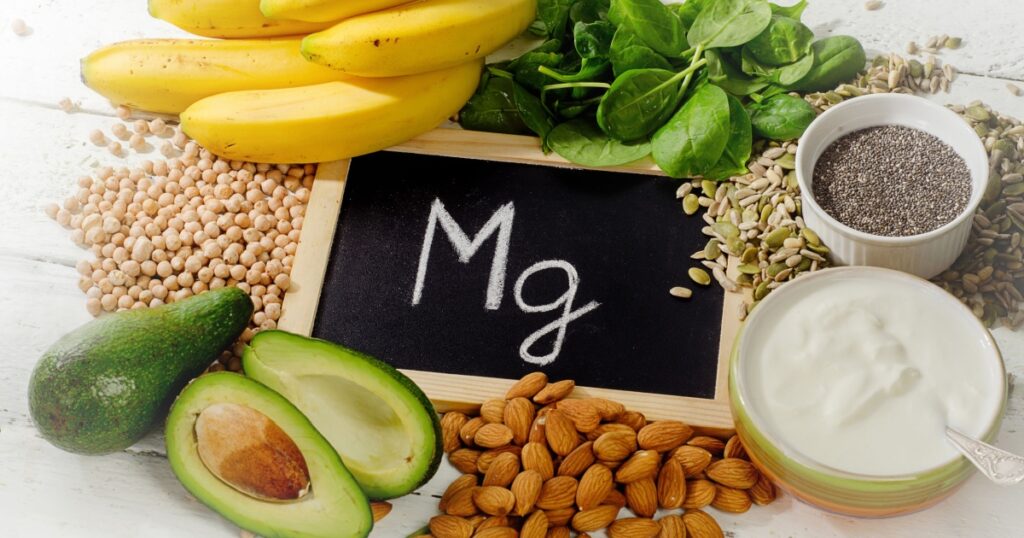
- Pumpking or Squash Seeds (317mg per quarter cup)
- Brazil Nuts (133mg per quarter cup)
- Salmon (92mg per 2.5k ounce fillet)
- Dry roasted Almonds (80mg in 1 ounce)
- Spinach (83mg per half cup, cooked)
- Black Eyed Peas (80mg per half cup)
- Swiss Chard (80mg per half cup, cooked)
- Tempeh (77mg per half cup)
- Dry roasted Cashews (74mg in 1 ounce)
- Oil Roasted Peanuts (63mg per quarter cup)
- Quinoa (63mg per half cup)
- Black Beans (60mg per half cup)
- Edamame (52mg per half cup)
- Avocado (44-55mg per 1 cup, cubed)
- Baked Potato with skin (43mg per 3.5 ounce potato)
- Brown Rice (42mg per half cup)
- Plain, Low fat Yogurt (42mg per 8 ounces)
- Instant Oatmeal (36mg per packet)
- Kidney Beans (35mg per half cup)
- Medium Banana (32mg)
The Bottom Line
If you do decide to go the supplementation route, be sure to talk to your doctor or health care provider before you start taking anything, in case of any possible interactions with medications. They can also help you to determine the amount you should be taking for your unique needs. Magnesium is crucial not only for our bodies to thrive and stay energized, but also to prevent many of the diseases that plague our society today. Eating a diet that includes plenty of magnesium-rich foods will prevent magnesium deficiency and lead to a healthier, happier you. If you still need some extra help and want relief that will last, Activation Ease naturally pure magnesium is the perfect solution. No digestive discomfort – just fast-acting 100% pure magnesium oil to soothe your pain and lower inflammation.
Read More: Why Up to 80% of Us are Deficient in Magnesium
Sources
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/#en52
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/research/resources/obesity/population/aric.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4549665/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3775240/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19271946?dopt=Abstract
- https://www.dietitians.ca/Your-Health/Nutrition-A-Z/Minerals/Food-Sources-of-Magnesium.aspx