Migraines are no fun, and they can greatly impact our daily lives. But did you know that they could be connected to your hormones, specifically serotonin? Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including mood, digestion, and blood flow. In recent years, researchers have discovered a significant link between serotonin levels and migraines. Understanding this connection can shed light on the causes of migraines and potentially lead to more effective treatment options.
What Is A Migraine?
Before diving into the link between migraines and serotonin, it is essential to understand what migraines are and how they differ from regular headaches. Unlike a typical headache, migraines are intense and often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Migraines can last anywhere from a few hours to several days, significantly impacting daily activities and quality of life. (1)
What causes a Migraine?
The exact causes of migraines are not fully understood, but researchers believe it is a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Hormonal changes, such as fluctuations in estrogen levels in women, have been found to trigger migraines in some individuals. Serotonin, a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating pain transmission and blood vessel constriction, also plays a significant role in migraine development.
The link between Migraines and Serotonin
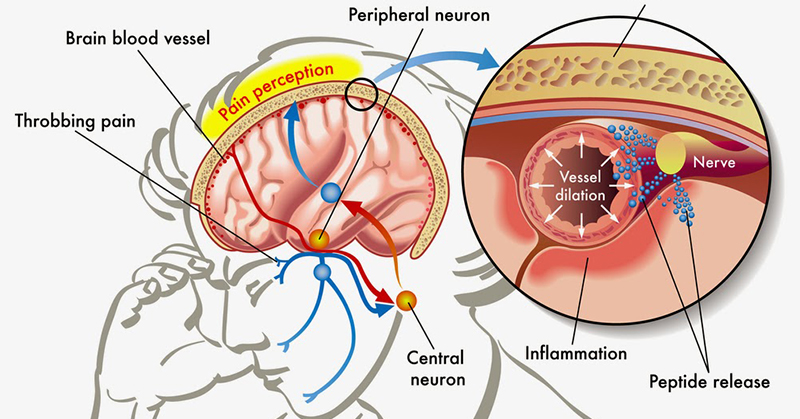
Serotonin levels in the brain have been found to be significantly altered during a migraine attack. Research has shown that during a migraine, serotonin levels drop, causing blood vessels in the brain to narrow (vasoconstriction) and then widen (vasodilation), leading to the throbbing pain associated with migraines. Additionally, an imbalance in serotonin levels can affect the brain’s pain processing centers, making individuals more sensitive to pain signals. (2)
Evidence suggests that serotonin receptors, specifically the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors, play a crucial role in migraine development. Activation of these receptors helps to regulate the release of various neurotransmitters, including serotonin, and can reduce the pain signals transmitted by the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the face to the brain.
Read More: 3 Vitamin Deficiencies Linked to Headaches
What you can do about it
Understanding the link between serotonin and migraines opens up potential treatment options. Medications that target serotonin receptors, such as triptans and ergotamine, have been developed to help alleviate the symptoms of migraines. These medications work by stimulating the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors, causing vasoconstriction of the blood vessels and reducing pain. (3)
In addition to medication, certain lifestyle changes can also help maintain serotonin levels and reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques can contribute to overall well-being and help manage serotonin levels. It is also important to identify and avoid triggers that can lead to migraines, such as certain foods, alcohol, and hormonal fluctuations.
The Bottom Line
Migraines are a complex condition with various contributing factors. The link between migraines and serotonin provides valuable insights into the underlying causes of migraines and potential treatment strategies. By targeting serotonin receptors and maintaining balanced serotonin levels through lifestyle changes, individuals can work towards managing and reducing the impact of migraines on their daily lives. As our understanding of migraines continues to evolve, it is hoped that further research will lead to even more effective treatments and support for those who suffer from migraines.
Read More: What Are Cervicogenic Headaches? How To Avoid These Headaches
Sources
- “How a Migraine Happens.” Hopkins Medicine
- “The evidence connecting migraine and mental health.” Medical News Today. Morgan Meissner, PhD. February 25, 2021.
- “Serotonin and CGRP in Migraine.” NCBI. Milan Aggarwal, Veena Puri and Sanjeev Puri, Ph.D. April 2012.