Did you know that NASA’s Voyager spacecraft has discovered a remarkable phenomenon at the boundary of our solar system? When NASA’s Voyager and its twin, Voyager 2, embarked on their epic mission in 1977, no one could have anticipated their discovery of a superhot “wall” at the very edge of the solar system. This blog explores this fascinating revelation, what it means for our understanding of space, and how these iconic spacecraft continue to shape our knowledge of interstellar exploration.
The Purpose of NASA’s Voyager Mission
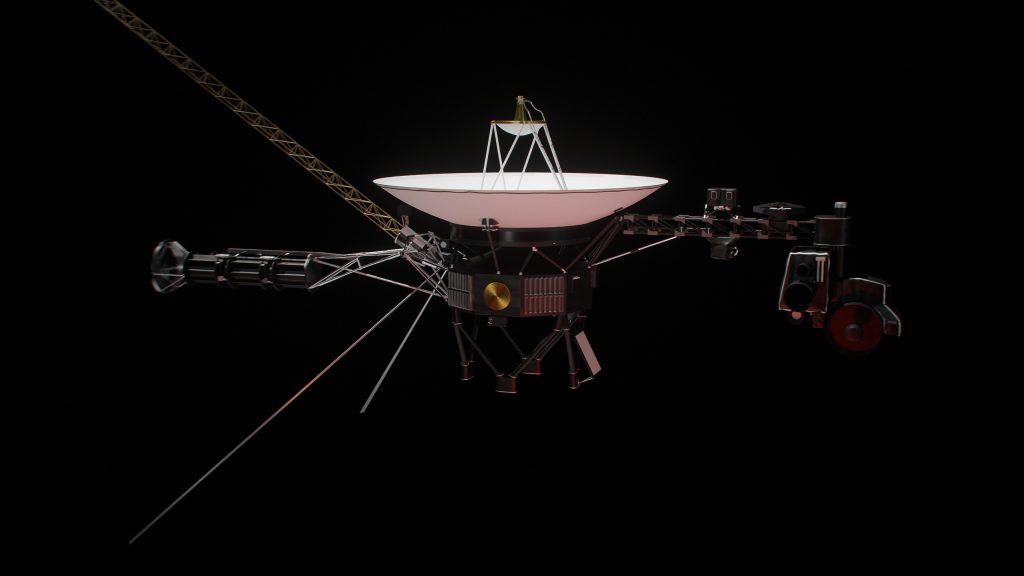

The Voyager program was designed to study the outer planets of our solar system, but its most astonishing contributions have come from its interstellar mission. With over 45 years of data, NASA’s Voyager has surpassed expectations, uncovering mysteries that defy our comprehension. The discovery of the superhot “wall” is one such breakthrough. Known as the heliopause, this area marks the boundary where the Sun’s influence ends, and the interstellar medium begins. This “wall” showcases extreme temperatures, ranging from 30,000 to 50,000 Kelvin, earning its nickname as the “wall of fire.”
What Is the Heliopause?
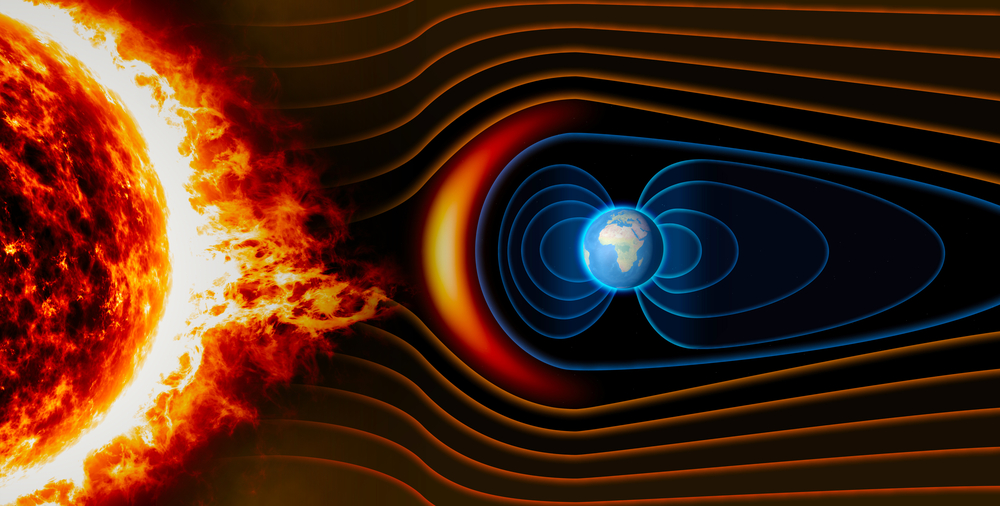
To understand the significance of this discovery, we need to explore the heliopause. The heliopause is the outermost edge of the Sun’s magnetic field, a bubble created by solar wind. This bubble, called the heliosphere, encompasses all the planets, shielding them from cosmic rays. Beyond the heliopause lies the interstellar medium, a vast expanse of space filled with charged particles, radiation, and mysteries waiting to be unraveled.
The Superhot Wall

When NASA’s Voyager crossed the heliopause, it encountered a region of extraordinarily high temperatures. This “wall of fire” is not a literal barrier but rather a boundary where particles collide, transferring heat and creating an energy-rich environment. At 30,000 to 50,000 Kelvin, this region is hotter than most stars’ surfaces, yet its particles are so sparse that heat transfer remains negligible.
How the Voyager Probes Survived
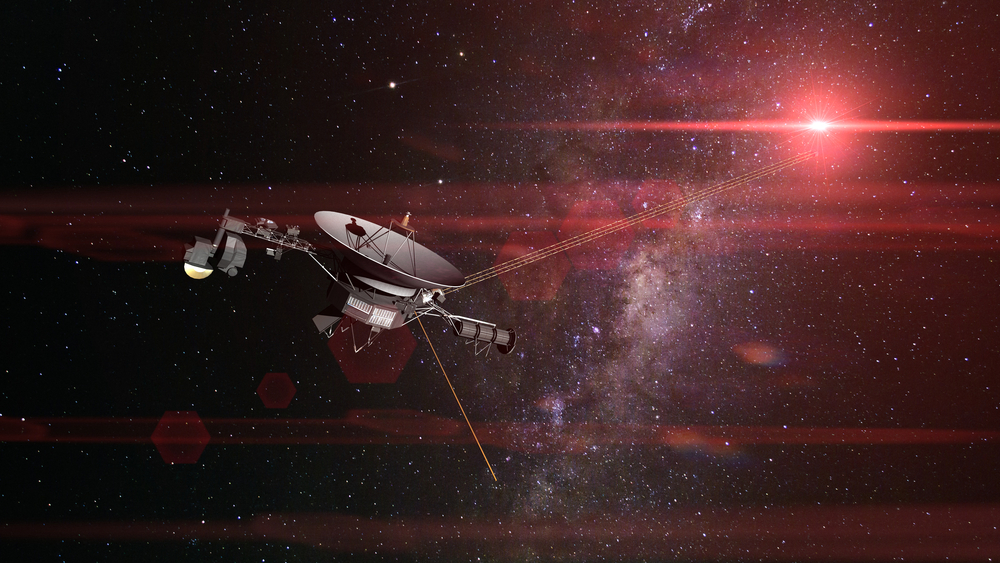

Remarkably, despite the extreme conditions, NASA’s Voyager probes have managed to survive and continue transmitting valuable data. Their robust engineering, reliance on nuclear power, and ability to function in low-density environments have enabled them to endure. The sparse particle collisions at the heliopause mean that even with such high temperatures, the physical effect on the spacecraft is minimal.
The Magnetic Field Revelation
Another groundbreaking finding from the Voyager probes was the discovery of aligned magnetic fields just beyond the heliopause. This revelation stunned scientists, as they had not anticipated such alignment between the Sun’s magnetic field and that of the interstellar region. This discovery has led to new questions about the nature of magnetic fields in space and how they interact on a cosmic scale.
The Legacy of Voyager’s Discoveries

The continued success of NASA’s Voyager has set the bar for interstellar exploration. These spacecraft are the first human-made objects to venture beyond the heliosphere, providing a glimpse into the interstellar medium. Their findings about the heliopause, interstellar particles, and magnetic fields have opened up entirely new fields of study, inspiring future missions to venture further.
Looking to the Future

The findings of NASA’s Voyager mission have not only expanded our understanding of space but have also laid the groundwork for new missions aimed at even deeper exploration. Missions like the Interstellar Probe, currently in development, aim to build upon Voyager’s legacy by reaching further into the cosmos. The data collected from the “wall of fire” and the heliopause will inform the design and objectives of future spacecraft.
Why This Matters

The discoveries made by NASA’s Voyager remind us of the importance of exploration and curiosity. The superhot wall and aligned magnetic fields highlight just how much there is to learn about the universe. They also illustrate the resilience of humanity’s desire to push boundaries and seek knowledge, no matter how distant or challenging the destination may be.
Final Thoughts

The journey of NASA’s Voyager spacecraft shows how much we can learn when we explore the unknown. These amazing probes have helped us understand where our solar system ends and the mysteries that lie beyond. Their discoveries at the edge of our solar system, like the superhot plasma and surprising magnetic fields, remind us that space is full of surprises. As new missions follow in Voyager’s footsteps, we are inspired to keep exploring and asking questions. Voyager’s story proves that human curiosity and creativity can take us farther than we ever imagined. The adventure isn’t over yet – there’s still so much more to discover!
Disclaimer: This article was created with AI assistance and edited by a human for accuracy and clarity.

