Developing unsightly varicose veins can make us feel self-conscious about our own legs. Up to 50 percent of women have varicose veins or a related venous disorder in the U.S. The large, swollen blood vessels are not just a cosmetic concern, they can pose a health risk, too.
What Causes Varicose Veins and How Can We Prevent Them?
In SciShow’s video, “Why Do I Have Varicose Veins?” Host Michael Aranda explains the body has over 160 thousand kilometers of blood vessels working hard to get oxygen to us so we can stay alive.
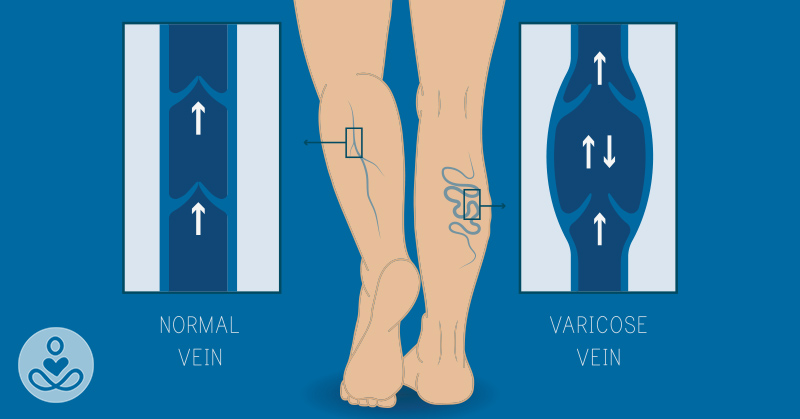
Arteries carry oxygen-loaded blood away from the heart and lungs, while veins take carbon dioxide-loaded blood back for recycling. Our circulatory system runs smoothly, but because the veins below our heart, especially the ones in our legs have to work against gravity, sometimes things can go wrong, like varicose veins.
Aging or gaining extra weight can make blood pool up and form lumpy varicose veins. Veins have a bunch of one-way valves to make sure blood flows toward the heart without backtracking, but there are a lot of ways these valves can stop working.
For example, when we age, our muscle fibers get thinner and weaker, so our vein valves can’t open and shut as smoothly anymore. Malfunctioning valves can also be hereditary so that genetics could be a factor.
Obesity can make us more prone to varicose veins because more body weight means more pressure on our legs, which can lead to higher blood pressure on our veins, known as can lead venous hypertension.
Vein walls are relatively thin compared to our arteries, meaning higher blood pressure can make our veins balloon out, and keep the valves from closing properly. The veins may swell up as a biological response as the body tries to handle the extra stress of high blood pressure.
Pregnancy can also cause varicose veins. Expectant mothers carry around extra blood to support a fetus, and the cocktail of pregnancy hormones can relax the walls of their blood vessels so that veins could bulge out more easily.
Tips for Treating Varicose Veins
There are 3 natural ways to reduce varicose veins, depending on its severity. For most people, these veins can be painful health issues. First, doctors suggest using compression clothing to help squeeze the legs like a tube of toothpaste, so the veins pump blood to your heart more easily.
Additionally, regular physical activity and a healthy, balanced diet can help offset the appearance of varicose veins on our legs, for a natural and fit look.
Other alternatives include laser treatment or sclerotherapy, where they inject a salt solution to irritating the vein, so the body seals it off.
However, it’s best to prevent varicose veins by moving around rather than sitting or standing still for hours. This will get the blood flowing throughout the body and promote healthy circulation.