Mold is a common problem in many households, but it’s not just the physical damage to your home that you should be worried about – it can also harm your health. Mold can easily become airborne and inhaled, leading to numerous respiratory and digestive issues. This is everything you need to know about mold in your home, how it could affect your health and that of your family – and what you can do about it.
Read: Most mattresses are filled with mold, mites and chemicals – here is how to know
Mold Exposure In Your Home Could Be Damaging Your Health
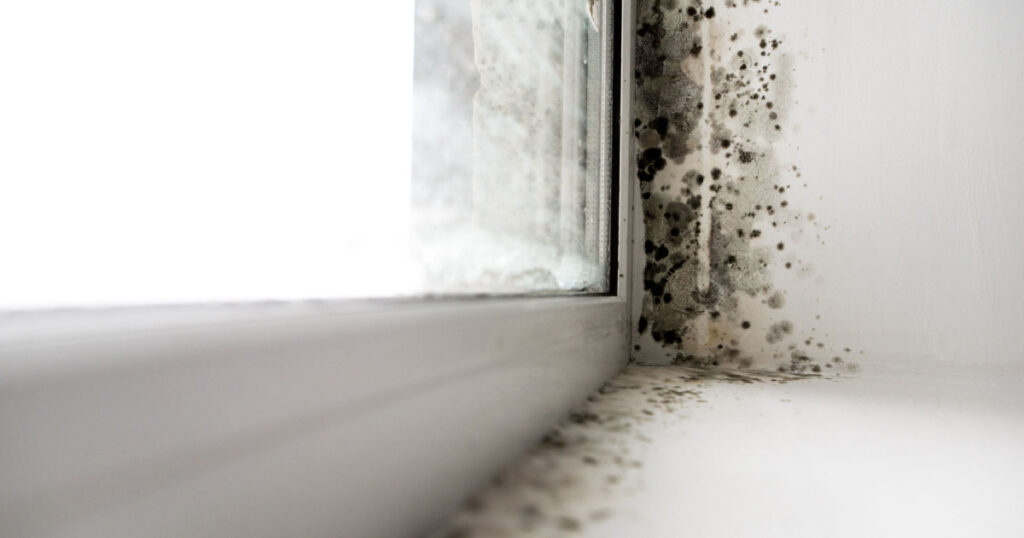

Mold is a fungus that grows in damp, humid areas such as bathrooms and basements. It likes to live in moist environments with little to no airflow. Mold can quickly spread throughout your home if it isn’t contained, making it very important to remove mold from your home as soon as possible. There are hundreds of different types of mold, however, the most commonly found in the home are (1, 2):
- Cladosporium: a brown, green, or black mold that grows in warm and cool locations. It’s normally found on wood, carpets, or fabrics and in heating and cooling ducts.
- Penicillium: a fuzzy mold that is blue, green, or yellow. It’s often found under carpets, in basements, and in insulation, especially when there’s been water damage.
- Aspergillus: a green, white, or gray with dark spots and a powdery look. This type of mold doesn’t need much ventilation. It can grow in fabrics, walls, attics, basements, and dry food items.
Once inhaled, the spores of these molds can manifest themselves in your body. Most commonly, they will affect either your lungs, sinuses, or digestive tract. Here are the symptoms and treatments for mold that can take root and grow in the lungs, sinuses, and digestive system.
Read: Woman’s Water Bottle Was ‘Poisoning’ Her For Weeks: Are You Making The Same Mistake?
Mold in the Lungs
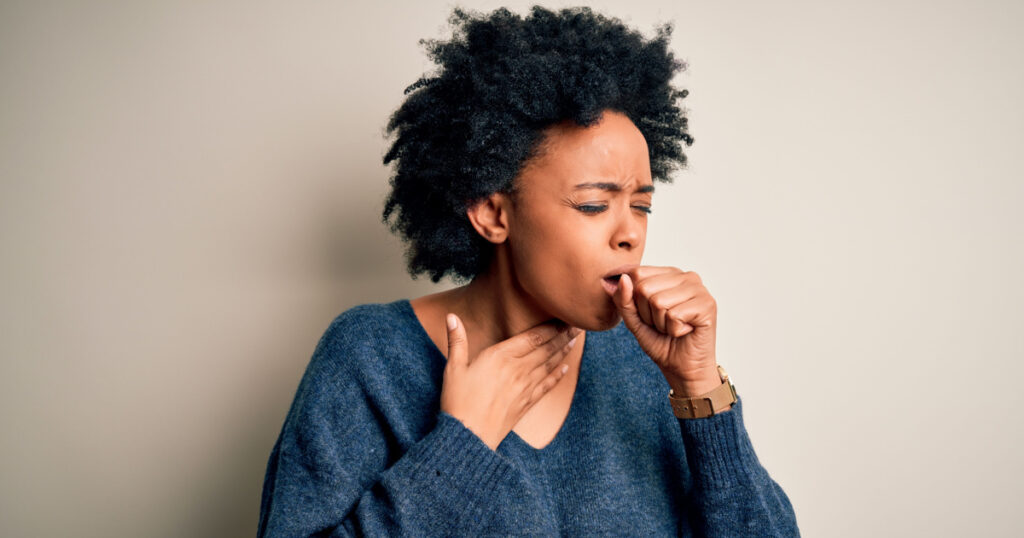

When mold spores become airborne and are inhaled, they can take root and grow in the lungs. They are particularly dangerous for those with pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma. Symptoms of this type of mold exposure can vary and may include:
- Coughing and wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness and pain
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever and chills
Diagnosing mold in the lungs can be challenging, as the symptoms are similar to other respiratory conditions. If you suspect mold exposure, the best thing to do is speak to your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Treatment options for mold in the lungs can include:
- Steroids and antihistamines to reduce inflammation and ease breathing
- Oxygen therapy if respiratory function is compromised
- Bronchodilators to aid in breathing
- Avoiding further exposure to mold
Read: Are Your Pillows Toxic?
Mold in the Sinuses
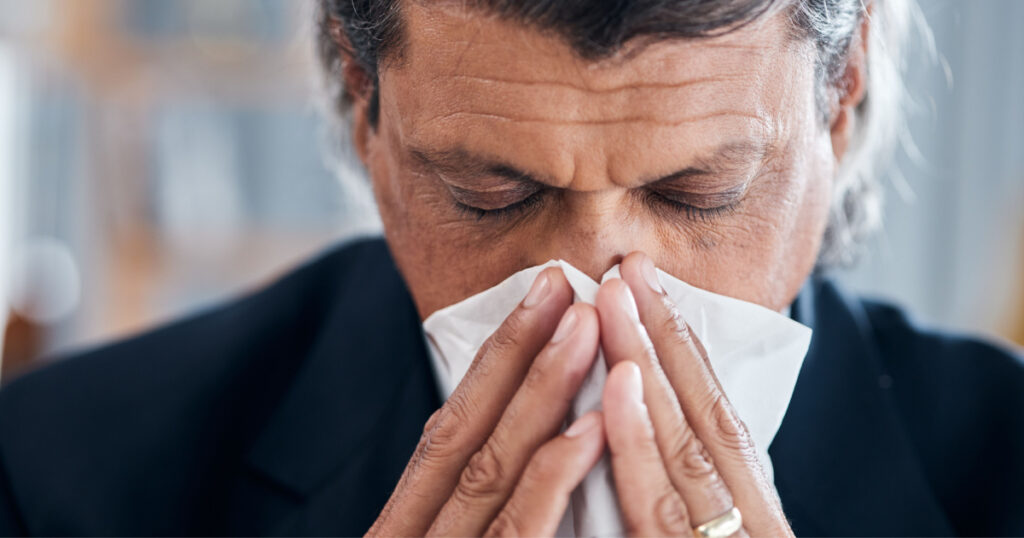

Mold can also take root and grow in the sinuses. They can potentially be a cause of chronic sinusitis. Symptoms of this type of mold exposure can include:
- Nasal congestion and stuffiness
- Postnasal drip
- Headaches
- Facial pressure and pain
- Decreased sense of smell
If you suspect mold exposure in your sinuses, a visit to an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) doctor is recommended for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment options for mold in the sinuses can include:
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays to relieve irritation and inflammation
- Antifungal medications to clear up an infection
- Surgical intervention in severe cases
Mold in the Digestive System
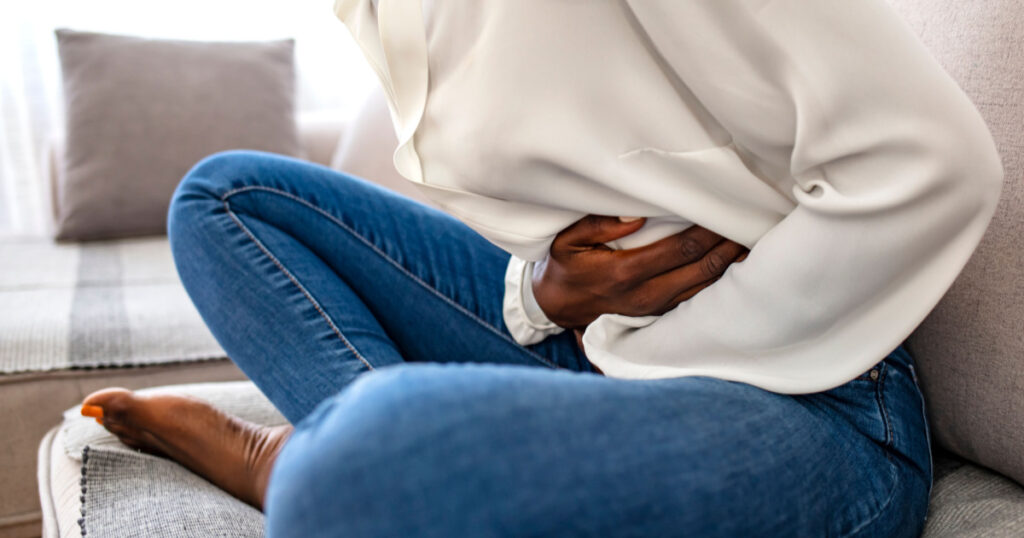

Mold can also take root and grow in the digestive system, particularly in people with weakened immune systems. Symptoms of mold exposure in the digestive system can include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Poor appetite and unintentional weight loss
If you suspect mold exposure in your digestive system, a visit to a gastroenterologist is recommended for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Read: Dollar Stores Are Full of Toxic Products
Treatment options for mold in the digestive system can include:
- Antifungal medications to clear up an infection
- Probiotics to restore healthy gut bacteria
- Avoiding foods that trigger symptoms
Prevention and Maintenance
The best way to prevent mold from taking root and growing in your body is to prevent exposure in the first place. Keep your home clean and dry to avoid the growth of mold. Fix any leaks or water damage immediately, and use a dehumidifier if your home is prone to excessive moisture. If you do encounter mold, it’s essential to address it promptly and effectively. Wear protective gear such as gloves and a mask when dealing with mold, and ensure the exposed area is properly ventilated.
There are also supplements you can take and things you can do to protect yourself in case mold unknowingly grows in your home. To address mold exposure, you can (3):
- Take antifungal medications
- Get allergy shots
- Use antihistamine sprays
- Spend time in the sauna to help remove toxins from mold via your sweat
- Try halotherapy (salt therapy)
- Take activated charcoal
Please remember that these are suggested treatments, with the last four being at-home treatments. They may or may not work, and you should always consult a medical professional before taking anything new. If you think you have been exposed to toxic mold, you are better off seeing a professional rather than trying to solve the problem on your own.
If You Find Mold, Remove It
Mold can be a serious health concern, particularly if it takes root and grows in the lungs, sinuses, or digestive system. If you suspect mold exposure and experience any of the symptoms mentioned, it’s important to speak with your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Take a proactive approach to prevent mold from growing and spreading in your home by practicing good maintenance and repair habits.
Keep Reading: How To Control Dust Mites In Your Home For Better Health
Disclaimer: This information is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and is for information only. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions about your medical condition and/or current medication. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking advice or treatment because of something you have read here.
Sources
- “Mold: Symptoms of Exposure, Risks, and More.” Healthline. Ann Pietrangelo. March 14, 2023.
- “Basic Facts about Mold and Dampness.” CDC
- “You Don’t Need to ‘Detox’ After Mold Exposure — Here’s What to Do Instead.” Healthline. Courtney Telloian. September 7, 2023.