Ginger is a popular spice that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. It is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects and is used to treat a variety of health conditions, including nausea, vomiting, and indigestion. However, despite its many benefits, ginger is not suitable for everyone, especially when using high doses and/or supplements. These are the groups who should avoid ginger for this reason.
Groups That Should Avoid Ginger

As already stated, ginger is an incredible plant. It has so many benefits for the human body. For this reason, indigenous groups have been using it for centuries for a number of ailments. Nowadays, ginger supplements are available. These are much more concentrated than what you would get from simply eating ginger root or using ginger powder. While ginger supplements can be beneficial, there are certain groups of people who should likely avoid them.
Read More: This is Why Most Ginger Ales Won’t Actually Settle Your Stomach
1. People with heart conditions
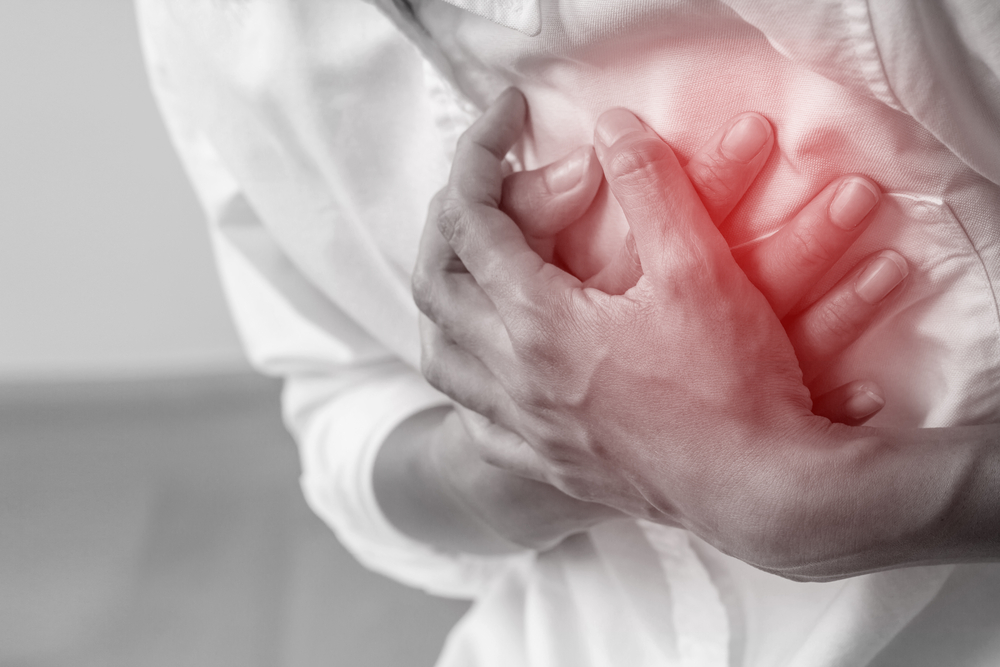

Ginger has been shown to lower blood pressure and improve circulation, which can be beneficial for some people. However, for people with heart conditions, this can be dangerous. Ginger can interact with certain medications used to treat heart conditions, such as blood thinners, and can increase the risk of bleeding. Additionally, ginger can cause arrhythmias in some people, which can be life-threatening. (1)
2. People with gallstones

Ginger has been shown to stimulate the production of bile, which can help improve digestion. However, for people with gallstones, this can be problematic. Bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. When the gallbladder is inflamed or has gallstones, the production of bile can be disrupted, leading to pain and discomfort. Ginger can exacerbate this condition by increasing the production of bile, which can cause further pain and discomfort. (2)
3. People with diabetes
Ginger has been shown to lower blood sugar levels, which can be beneficial for people with diabetes. However, ginger can be dangerous for people taking medications to lower their blood sugar levels. Ginger can interact with these medications and cause blood sugar levels to drop too low, leading to hypoglycemia.
“We know that ginger can affect your insulin levels … so it can interact with certain diabetes medications people are on; if you’re taking ginger supplementation and you are on diabetes medication, that can cause low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia,” says Rahaf Al Bochi, RD, a spokesperson for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and owner of Olive Tree Nutrition. (3)
Read More: 10 Reasons to Make Ginger Syrup and Use it Every Day (with recipe!)
4. Anyone experiencing severe side effects

While ginger is generally safe for most people, some people may experience severe side effects. These can include allergic reactions, such as hives or difficulty breathing, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. If you are experiencing severe side effects after consuming ginger, you should stop using it immediately and seek medical attention.
5. Possibly if You’re Pregnant

The message regarding ginger and pregnancy is mixed. While some studies have shown that ginger can be safe and effective for treating morning sickness (4,5), other studies have raised concerns about the safety of high doses of ginger and ginger supplements during pregnancy. Some evidence indicates that ginger tea should not be consumed close to labor, as it may increase bleeding risk. Pregnant women with a history of miscarriages, vaginal bleeding, or blood clotting issues should also stop using ginger products(6).
It is generally recommended that pregnant women avoid high doses of ginger and ginger supplements and instead consume ginger in moderation as part of their regular diet. This, for example, could be in the form of ginger tea. This is easily made by steeping slices of fresh ginger in hot water. Add some lemon and honey for added flavor and nutritional benefits.
The Bottom Line

While ginger has many health benefits, it is not suitable for everyone. People with heart conditions, gallstones, diabetes, and anyone experiencing severe side effects should avoid using ginger. Pregnant women should also use caution when consuming ginger and should consult with their healthcare provider before using ginger supplements. As with any supplement or medication, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider before using ginger to ensure that it is safe for you.
Supplementation always has the possibility of going wrong due to high doses, if you notice any adverse effects, speak with your healthcare provider. Again, if you want some of the benefits of ginger with a very low risk of side effects, simply use the ginger root itself.
Read More: How Might Ginger Help with Obesity and Fatty Liver Disease?
Sources
- “Ginger.” Mount Sinai
- “What are the side effects of ginger tea?” Medical News Today. Lydia Kibet. November 30, 2020
- “The Potential Health Benefits and Risks of Ginger for Type 2 Diabetes.” Everyday Health. Jamie Ludwig. January 16, 2018
- “The Effectiveness of Ginger in the Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting during Pregnancy and Chemotherapy” Integrative Medicine Insights. March 31, 2016
- “How Safe Is Ginger Rhizome for Decreasing Nausea and Vomiting in Women during Early Pregnancy?” Foods. April 1, 2018
- “Ginger for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy” Can Fam Physician

