Heart disease, one of the leading causes of death worldwide, often manifests through subtle symptoms that can be easily overlooked or mistaken for less serious conditions. Among these, a specific sign of heart disease —sleep apnea—has gained significant attention for its strong association with cardiovascular problems. Recognizing and addressing this symptom can be crucial in preventing severe health outcomes.
Understanding One of The Biggest Signs of Heart Disease – Sleep Apnea

Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, known as apneas, can last for a few seconds to a minute and can occur dozens or even hundreds of times per night. The most common type, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively, leading to a temporary blockage of the airway.
Read More: Getting up to pee often in the night could be a symptom linked to heart failure, research says
The Link Between Sleep Apnea and Heart Disease

Several studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between sleep apnea and cardiovascular diseases. Individuals with untreated sleep apnea are at a higher risk for conditions such as hypertension, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and stroke. The repeated apneas cause a drop in blood oxygen levels, prompting the brain to wake the body up just enough to resume breathing. This results in fragmented sleep and significant stress on the cardiovascular system.
How Sleep Apnea Affects the Heart
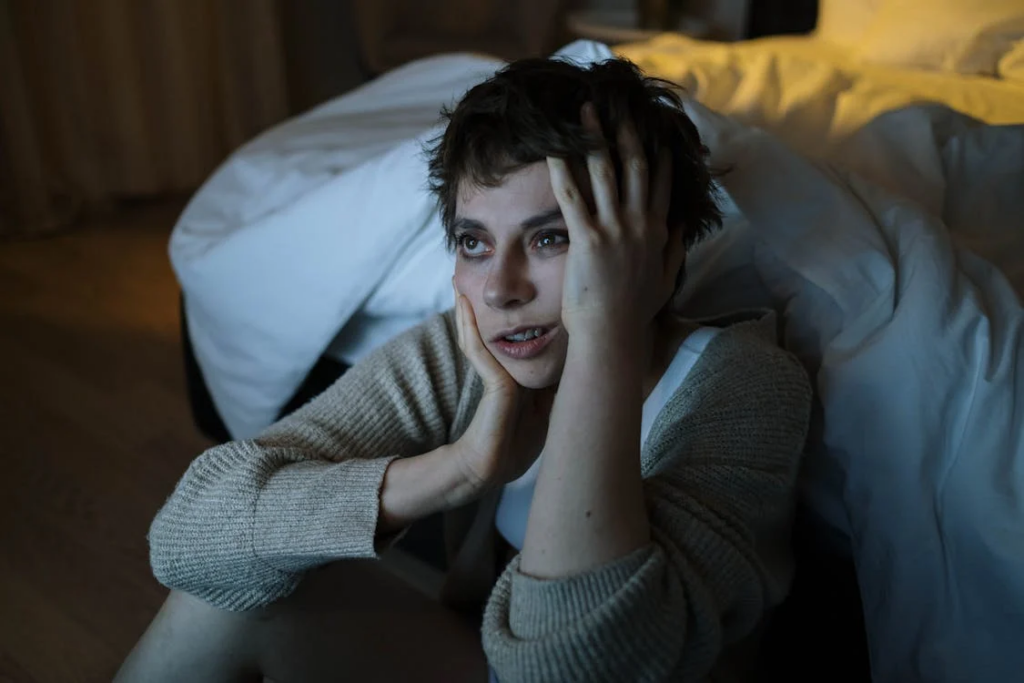

During an apnea event, the lack of oxygen causes the body to release stress hormones like adrenaline, which can increase blood pressure and heart rate. Over time, these repeated surges in blood pressure can damage the arteries and lead to chronic hypertension. Additionally, the frequent awakenings associated with sleep apnea prevent the heart from getting the restorative rest it needs, exacerbating cardiovascular strain and promoting heart disease.
Recognizing the Symptoms
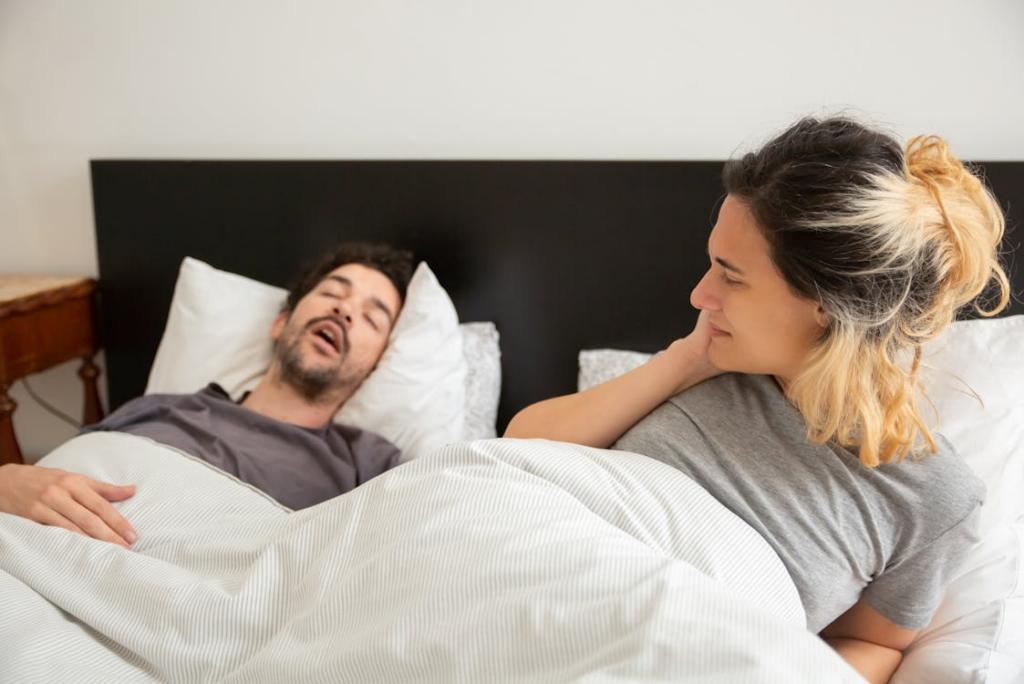

One of the most telling signs of sleep apnea is loud, chronic snoring, often accompanied by gasping, choking, or snorting sounds during sleep. Other symptoms include excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. It is essential for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical evaluation, as early diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
The Importance of Diagnosis

Diagnosing sleep apnea typically involves a sleep study, either conducted at a sleep center or through a home sleep apnea test. These studies monitor various physiological parameters, including breathing patterns, oxygen levels, heart rate, and brain activity, to determine the presence and severity of sleep apnea. Identifying and quantifying the condition is a critical step in managing both sleep apnea and its cardiovascular implications.
Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
The primary treatment for sleep apnea is the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, which involves wearing a mask over the nose and/or mouth during sleep. The mask delivers a steady stream of air that keeps the airway open, preventing apneas and ensuring uninterrupted breathing. Other treatment options include lifestyle changes such as weight loss, positional therapy to prevent sleeping on the back, and in some cases, surgical interventions to remove airway obstructions.
Read More: A Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Could Be Warning You With These 9 Signals
Lifestyle Modifications and Heart Health

Addressing sleep apnea is just one aspect of maintaining heart health. Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in reducing the overall risk of heart disease. These include adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. For individuals with sleep apnea, these changes can complement CPAP therapy and further alleviate cardiovascular strain.
The Role of Regular Medical Check-ups

Regular medical check-ups are essential for early detection and management of both sleep apnea and heart disease. Healthcare providers can monitor vital signs, conduct necessary tests, and provide guidance on managing risk factors. For those diagnosed with sleep apnea, ongoing follow-up care ensures that treatment remains effective and any emerging cardiovascular issues are promptly addressed.
Conclusion: A Proactive Approach to Health At The First Sign of Heart Disease

Recognizing sleep apnea as a significant nighttime symptom of heart disease underscores the importance of a proactive approach to health. By being aware of the symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention, individuals can effectively manage sleep apnea and reduce their risk of developing serious cardiovascular conditions. Comprehensive care, including proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, plays a vital role in promoting long-term heart health and improving overall quality of life.
In summary, sleep apnea is more than just a sleep disorder; it is a potential indicator of underlying heart disease. Understanding this connection and taking appropriate action can make a significant difference in preventing and managing cardiovascular problems, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and a longer, healthier life.
Read More: Heart Disease: 10 Warning Signs that Appear On Your Skin
Sources
- “The red flag signs at night that could be signalling heart disease” Express. Fiona Callingham. December 13, 2023.
- “How Are Heart Failure and Sleep Related?” Web MD
- “Sleep Problems Related to Heart Failure and How to Manage Them” Everyday Health. Rita Colorito. September 23, 2022.
- “Sleep Disorders: Heart Disease” UCLA Health