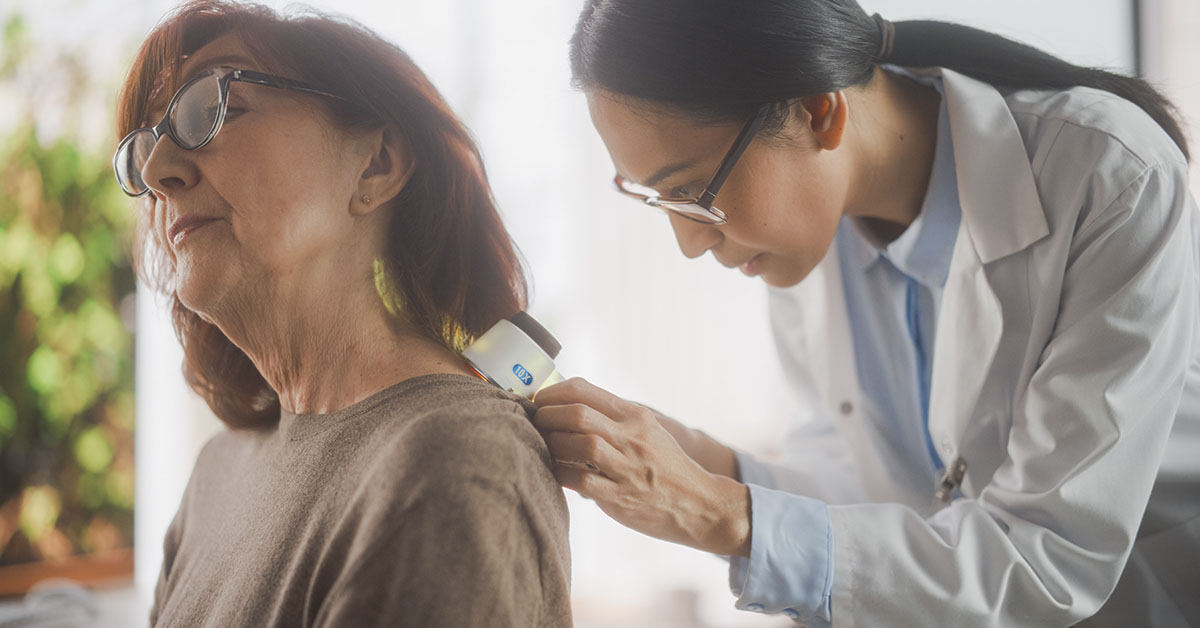
Skin cancer is caused by the growth of abnormal cells in your skin tissues. It is the most commonly diagnosed type of cancer in the United States. In fact, around one in every five individuals will be diagnosed with skin cancer at some point in their lives. However, skin cancer is also among the most easily detected and treated forms of the disease. The most common warning sign is the appearance of a new growth or a change in an existing one. Symptoms of skin cancer include a waxy or pearly facial bump, areas on the skin that look like scars, wounds that won’t heal, and a new mole. In this article, we will take a deeper look at five things you should know about skin cancer.
UV Exposure Prevention Counseling Is Important
One of the biggest skin cancer risk factors is exposure to ultraviolet rays. The UV rays that come from tanning beds and the sun can result in skin cell DNA damage. Constant exposure to UV rays, especially during childhood, can increase your risk of developing melanoma. The Preventive Services Task Force in the United States recommends counseling to children and young adults that promotes using protective measures against the sun. A systematic review of the impact of counseling in children and adults found that it led to an increase in preventative behaviors and self-examination. In adults, it also led to more skin procedures.
Early Detection Saves Lives
Melanoma is responsible for the most cancer deaths, yet only accounts for only 1% of skin cancer cases. This is why early detection is so important, as the disease is very treatable at the early stages. When the melanoma is still localized to one spot, the survival rate after diagnosis and treatment is 99%. However, this number drops to 75% when it has begun to spread, and 35% when it has reached distant parts of the body. The best way to self-examine is to use the “ABCDEs”. The “A” is for asymmetry – when two halves of a mole are uneven. The “B” represents the border, where jagged edges may cause concern. The “C” is for uneven coloring, and the “D” is for the mole’s diameter. It should typically be no larger than a pencil eraser. The “E” stands for evolving, meaning there is constant change in the mole’s appearance.
Read More: Anal Cancer On the Rise, Study Highlights Most Vulnerable Population
Most Common Cancer In The United States
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, around 9500 individuals are diagnosed with skin cancer every single day. From 1976 to 2010, incidences of squamous cell carcinoma increased by 263% and basal cell carcinoma by 145%, with women exhibiting a greater increase than men. Incidence of melanoma is likewise increasing, with more than 1 million people in the United States currently diagnosed with the disease. While melanoma rates for younger adults have declined, the number of cases continues to rise for those over the age of 50.
Skin Cancer Detection Technology Is Advancing Rapidly

Recent studies have shown that artificial intelligence can substantially improve skin cancer diagnosis accuracy. Research conducted by Stanford Medicine revealed that AI models trained on thousands of images helped health care practitioners detect cancers more effectively. This proved to be true even for those individuals who were not trained dermatologists. While the aim is not for the AI to replace physicians, using it to help make clinical decisions could prove hugely beneficial. In fact, AI would be particularly useful in this case, since dermatology is reliant on visual assessments. Experts say that it could improve outcomes for all patients due to a reduction in physician burnout and a boost in diagnostic accuracy.
Late Diagnosis Often Occurs In Darker-Skinned Patients
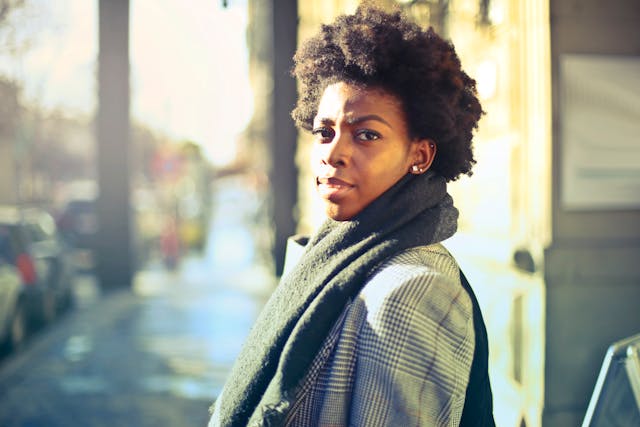

One might assume that darker skin would offer more protection from developing skin cancers. However, melanoma can affect anyone and is typically diagnosed later in darker-skinned individuals. This often makes it harder to treat. Even though melanoma is less prevalent in black, Pacific Islander, and Asian individuals than white individuals, the rates of survival are actually lower. In black individuals, the cancer is often only discovered once it has already spread to other organs or the lymph nodes. Darker-skinned patients are also more likely to get melanoma on parts of the body not typically exposed to the sun. This includes under the nails, inside the mouth, and on the soles and palms.
Read More: Modified Himalayan Fungus Compound Boosts its Anti-Cancer Properties 40x

