The recent discovery of a Mesoamerican fertility site deep inside a remote cave in Guerrero, Mexico, has captivated archaeologists worldwide. Located in the Tlayócoc Cave high in the mountains, this site contains artifacts linked to fertility rituals practiced over 500 years ago. The cave’s near-inaccessibility helped preserve its contents in remarkable condition, offering a rare glimpse into the spiritual life of a little-known Mesoamerican culture. This find sheds new light on ancient ceremonial traditions, the sacred role of caves, and the diversity of pre-Hispanic peoples in the region.
The Discovery of Tlayócoc Cave
In September 2023, speleologists Yekaterina Katiya Pavlova and Adrián Beltrán Dimas explored the Tlayócoc Cave, situated approximately 7,800 feet above sea level in Guerrero. Expecting to find modern debris, they instead uncovered a carefully arranged collection of artifacts placed atop small stalagmites deep within the cave. The site had remained largely untouched for centuries due to its difficult access, involving narrow passages and low air space. Recognizing the significance of their find, the explorers realized they had stumbled upon a sacred fertility site, offering unique insights into ancient spiritual practices.
Artifacts Unearthed and Their Symbolism
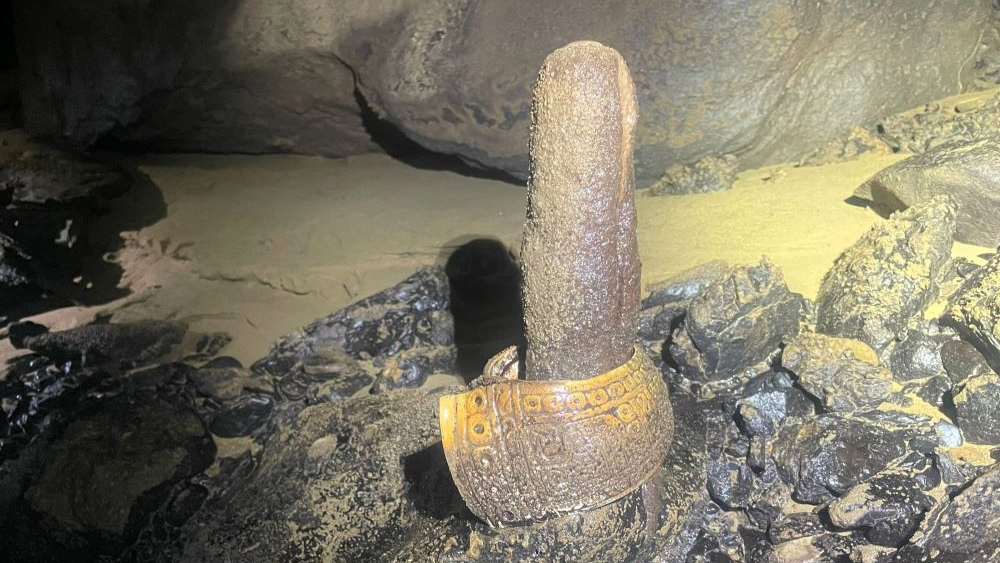

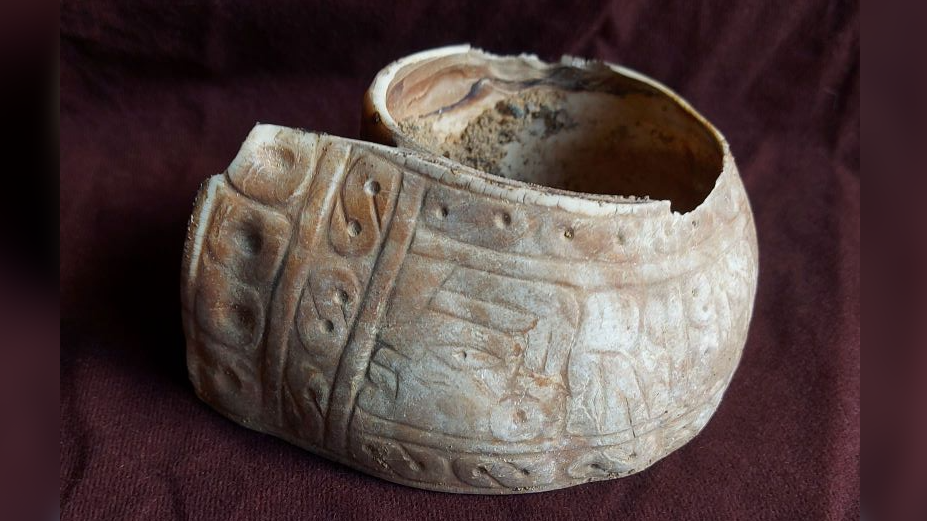
The archaeological team recovered 14 artifacts including four shell bracelets– three engraved with images of the planet Venus and the god Quetzalcoatl- two stone disks resembling ritual pyrite mirrors, a large decorated sea snail shell, and fragments of charred wood. The careful placement of these items on phallic-shaped stalagmites underscores their ritual importance. The celestial and deity symbols highlight the role of divine forces in fertility ceremonies, providing rare evidence of how ancient peoples sought blessings for prosperity and reproduction through sacred offerings.
The Spiritual Significance of Caves in Mesoamerica
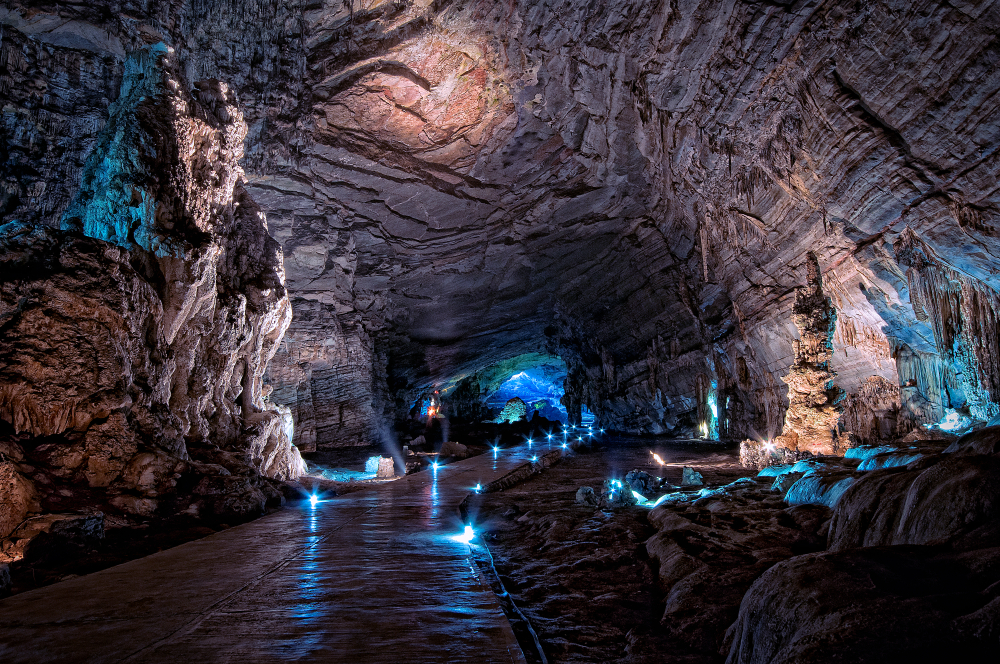

Caves held profound spiritual meaning for many Mesoamerican cultures. Often regarded as entrances to the underworld and places of transformation, caves were believed to house powerful forces connected to fertility, rain, and life cycles. The remote and hidden nature of Tlayócoc Cave made it an ideal location for secret ceremonies. Ancient peoples used such sites to connect with gods and ancestors, seeking blessings for crops, animals, and family growth. This discovery reinforces the understanding that natural landscapes were central to their spiritual worldview.
Fertility Rituals and Their Cultural Importance

Speleologist Katiya Pavlova explains how this discovery was made, in a translated statement. “I looked in, and it seemed like the cave continued. You had to hold your breath and dive a little to get through. That’s when we discovered the two rings around the stalagmites.”
The “rings” turned out to be shell bracelets that were possibly used in fertility rituals over 500 years ago.
Fertility was vital to survival and prosperity in Mesoamerican societies. The artifacts found suggest rituals involving offerings to deities to ensure healthy crops, animals, and families. The presence of mirrors symbolized reflection and divine vision during ceremonies. This likely included prayer, music, and symbolic gestures to invoke fertility powers. This Mesoamerican fertility site is one of the few direct archaeological links to these ancient practices, helping scholars understand how such rituals shaped social and religious life.
Read More: Scientists Uncover Mysterious Tunnels Belonging to an Unknown Ancient Lifeform
Insights into a Little-Known Culture

The artifacts are attributed to the Tlacotepehua culture, a little-known group that thrived around 500 years ago in Guerrero. Unlike the well-documented Aztec or Maya civilizations, this culture remains largely mysterious. The cave’s findings provide rare insight into their beliefs and customs.
INAH archaeologist Miguel Pérez Negrete explained in the statement, “For pre-Hispanic cultures, caves were sacred places associated with the underworld and considered the womb of the Earth.”
Ultimately, this reveals shared spiritual themes such as celestial worship and fertility gods, but with unique ritual expressions tied to this isolated cave setting. This discovery broadens knowledge of Mesoamerican cultural diversity and highlights the many ancient groups still under-researched in Mexico’s rugged landscapes.
The Role of Remote Caves in Ritual Practice

Remote caves like Tlayócoc were ideal for private religious ceremonies, away from everyday life. Their isolation and natural features enhanced their mystical importance. Such caves served as sacred spaces for rituals related to fertility, rain, and agriculture. Archaeologists study these Mesoamerican fertility sites to understand the religious beliefs and practices that shaped Mesoamerican societies. There is a profound connection between people and their environment, and sites like these prove that.
Expanding Our Understanding of Mesoamerican History

This discovery challenges previous assumptions about the complexity of lesser-known ancient cultures in the region. The unique style and symbolism of the artifacts suggest a diversity of traditions beyond the major Mesoamerican civilizations. It underscores how much remains hidden in remote locations and the importance of exploring similar caves to uncover lost histories. The find adds valuable details to the broader narrative of Mesoamerican civilizations and their relationship with nature and fertility.
Contemporary Significance and Future Research

The Tlayócoc fertility site not only enriches historical knowledge but also highlights the importance of preserving sacred places. Its remote location suggests that spiritual practices were deeply personal and secretive. Modern archaeology benefits from such discoveries by filling gaps in history and fostering appreciation for cultural diversity. Ongoing research promises further insights, inspiring protection efforts for similar sites and deepening understanding of ancient human connections to nature.
Conclusion

The discovery of the Mesoamerican fertility site in Tlayócoc Cave opens a remarkable window into ancient life and spirituality. The unique artifacts reveal a culture deeply invested in fertility rituals and the sacredness of natural landscapes. This find adds invaluable knowledge about lesser-known Mesoamerican groups and their ceremonial traditions. Preserving and studying this site allows future generations to learn from these hidden treasures. It also helps us to gain new perspectives on the rich tapestry of human history.
Read More: Stunning Ancient Egyptian Artifacts Unearthed in Secret Chamber 14 Meters Underground
Disclaimer: This article was created with AI assistance and edited by a human for accuracy and clarity.

