Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is an essential nutrient for various bodily functions, including immune system regulation, nerve function, and energy metabolism.1 Despite it being important to our overall health, a large portion of the population is likely deficient in this vitamin, which leads to various health issues.2 Here are six signs that indicate low levels of vitamin B6 in the body and how to address its deficiency.
1. Mood Changes

One of the main indicators of a vitamin B6 deficiency is mood changes. Individuals with a deficiency may experience confusion, irritability, anxiety, and even bouts of depression. Research suggests that adding supplements can alleviate anxiety and depression, which shows how important the vitamin plays in mental well-being.
Read More: Scientists Reveal New Findings About Older Adults Who Take Vitamin D
2. Mouth and Tongue Changes

A Vitamin B6 deficiency can often manifest in oral health issues like sores, cracked lips, and an inflamed tongue. These symptoms (collectively known as cheilosis and glossitis) can cause serious discomfort and difficulty eating and/or speaking. Addressing the deficiency is easy enough with dietary changes or supplementation. They’re easy fixes but are crucial to resolving these oral issues.
3. Skin Rashes

Seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by red, flaky skin rashes and is another common symptom of a vitamin B6 deficiency.3 This is due to the vitamin’s role in collagen synthesis, which is essential for maintaining healthy skin. This is why a B6 deficiency can lead to several dermatological issues. Ensure you get an adequate intake of vitamin B6-rich foods (supplement only if needed) to help alleviate skin problems associated with deficiency.
Read More: Vitamin B12 Deficiency Symptoms that Most People Ignore
4. Anemia

Vitamin B6 also plays a major role in our hemoglobin production, so its deficiency can lead to microcytic anemia (AKA anemia). Symptoms of anemia (amongst other things) include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, so detecting and addressing a deficiency is essential in managing and restoring optimal blood health.
5. Peripheral Neuropathy
Nerve damage, known as peripheral neuropathy, is a much more severe consequence of a vitamin B6 deficiency. This condition can cause tingling, numbness, and even muscle weakness in our extremities. Early intervention can be done through supplementation and adjustments in diet to prevent further nerve damage and alleviate symptoms. But make sure if you are experiencing these symptoms to get yourself checked.
6. Ataxia
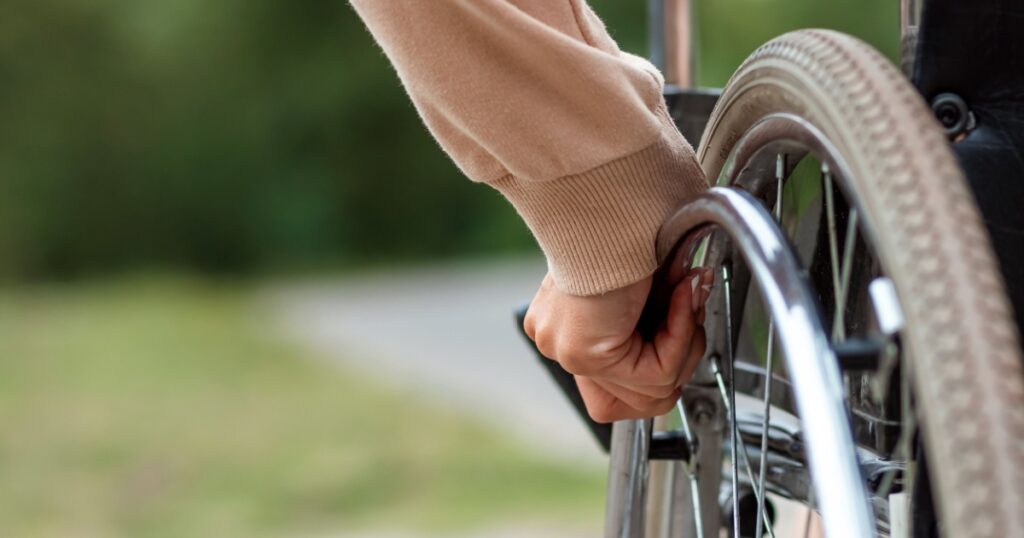

In more severe cases, a vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to ataxia, which is a loss of muscle control. Symptoms of ataxia include an impaired sense of balance, difficulties with coordination, and slurred speech. Getting a timely diagnosis and treatment for a deficiency is crucial in preventing devastating neurological complications like ataxia.
The Bottom Line

Recognizing the signs of a vitamin B6 deficiency is incredibly important for maintaining our overall health and well-being. From mood changes to oral issues, anemia to nerve and muscle failure, this vitamin has a hand in several key attributes of our health. Either by dietary or supplemental efforts, addressing a deficiency can seriously improve one’s quality of life and prevent long-term health complications. Be sure to consult a healthcare provider if you suspect a vitamin B6 deficiency in yourself or anyone you know. A doctor can best provide recommendations and guidance based on your specific needs. If you prioritize proper vitamin B6 intake, you can support the essential functions and promote optimal health and vitality.
Read More: 9 Early Warning Signs Your Body is Low in Vitamin-C
Sources
- “Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency.” Health. Laura Dorwart. March 14, 2024.
- “Vitamin B6.” NIH
- “9 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency.” Healthline. Marsha McCulloch, MS, RD. June 25, 2023
Disclaimer: This information is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and is for information only. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions about your medical condition and/or current medication. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking advice or treatment because of something you have read here.

