Ear infections are a common and often painful condition that affects people of all ages. They occur when the middle ear becomes inflamed and infected, usually due to bacterial or viral infections. If left untreated, ear infections can cause serious complications and even lead to hearing loss. In this article, we will discuss the signs that indicate you may have an ear infection and provide tips on how to prevent them.
What is an Ear Infection and What Causes Them?
An ear infection, also known as otitis media, occurs when bacteria or viruses enter the space behind the eardrum and cause an infection. This can happen due to a respiratory infection, allergies, or a blocked Eustachian tube. This is the tube in the ear that is responsible for equalizing pressure in the middle ear. Children are more prone to ear infections because their Eustachian tubes are smaller and more easily blocked. (1)
Read More: 7 Signs That Death May Be Near in Someone With Dementia
Different Types of Ear Infections
There are three main types of ear infections: acute otitis media (AOM), otitis media with effusion (OME), and chronic otitis media with effusion (COME). AOM is the most common type and is characterized by sudden onset of symptoms such as ear pain, fever, and fluid buildup behind the eardrum. OME occurs when fluid remains trapped in the middle ear after an infection has cleared, while COME is a long-lasting inflammation of the middle ear. (2)
6 Signs You Have an Ear Infection

While you may think ear infections are obvious, this is not always the case. This is especially so with children, who may present differently or have trouble communicating their symptoms. Knowing the signs of an ear infection can help you seek treatment as early as possible, limiting discomfort and also the potential for complications. The following are the primary ear infection symptoms (3):
1. Pain or Discomfort

Ear pain is the most common symptom of an ear infection. It may be sharp or dull and can worsen when lying down or chewing. Babies and young children may tug at their ears or become irritable and fussy.
2. Itchiness

Itchy ears can be a sign of an ear infection, especially if accompanied by pain or discomfort. Scratching the ears can exacerbate the problem and increase the risk of infection.
3. Redness on Both Inner and Outer Parts of the Ear
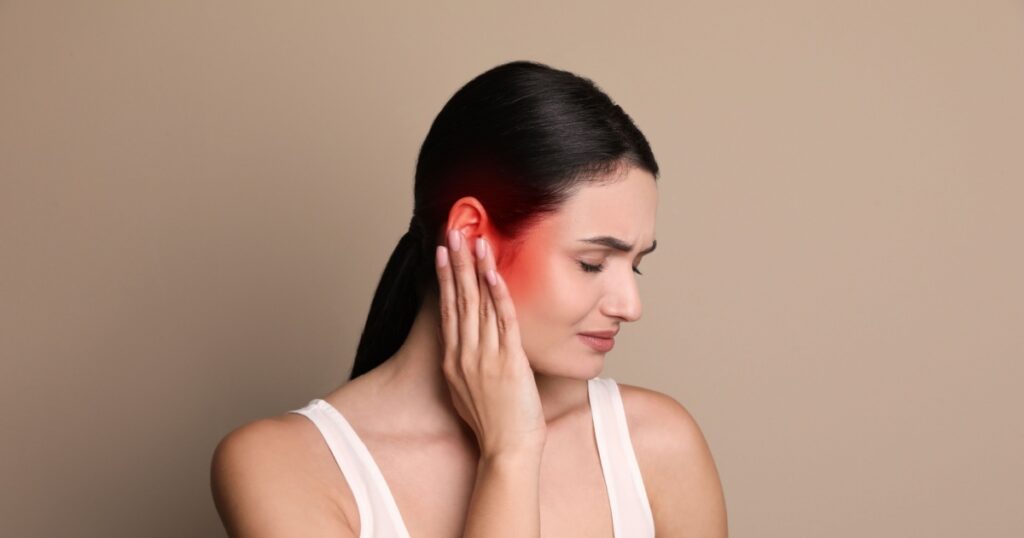
Inflamed and red ears, both on the inside and outside, are another sign of an ear infection. The skin may also feel warm to the touch.
Read More: Early Warning Signs Your Body Needs Vitamin-C
4. Drainage of Odorless Fluid from the Ear
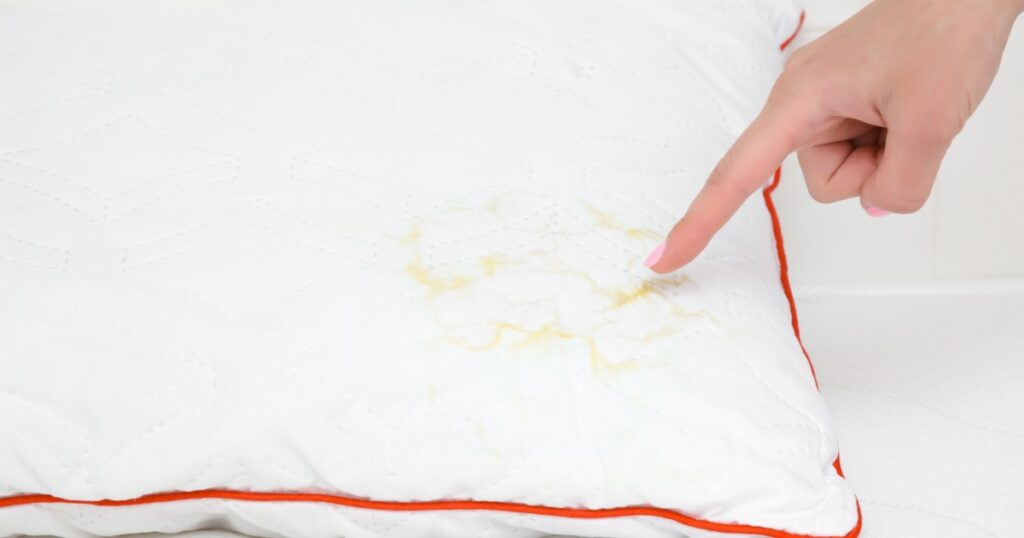

If you notice clear or slightly yellow fluid draining from the ear, it may indicate a middle ear infection. This fluid is usually odorless and can stain pillows or clothing.
5. Muffled Hearing or Ringing Sound in Ears

A buildup of fluid in the middle ear can affect hearing and cause a muffled or blocked sensation. Some people may also experience a ringing or buzzing sound, known as tinnitus.
6. Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Neck
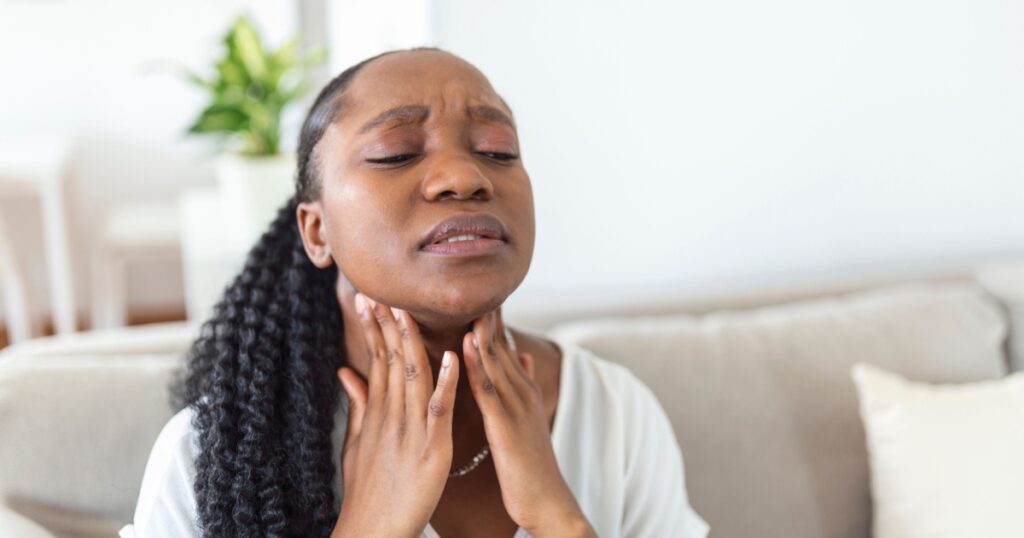

In some cases, an ear infection can cause the lymph nodes in the neck to become swollen and tender to the touch. This is a sign that the body is fighting off an infection.
What to Do If You Think You Have an Ear Infection
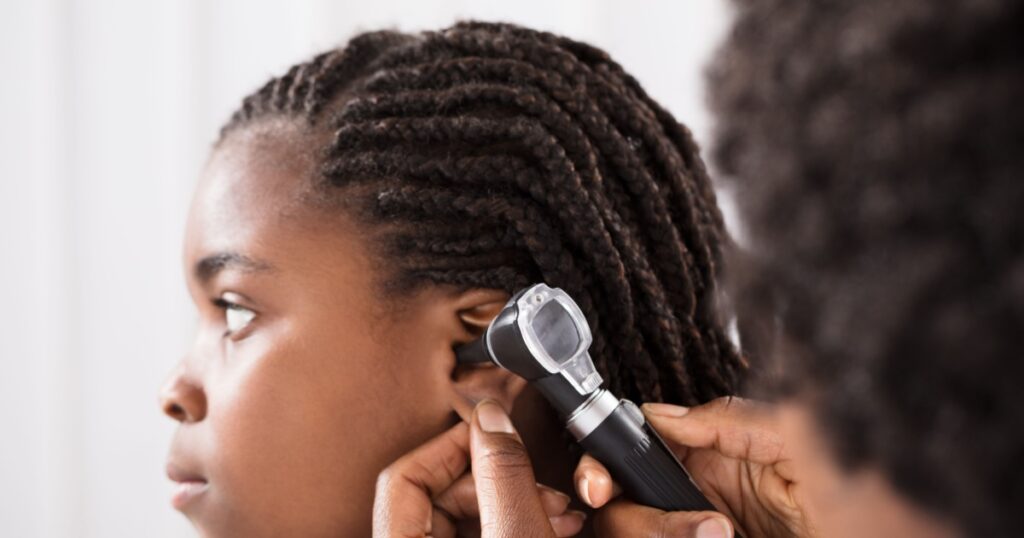

If you suspect you have an ear infection, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional will examine your ears using an otoscope to determine the cause and severity of the infection. They may prescribe antibiotics if the infection is bacterial or recommend over-the-counter pain relief medication to alleviate symptoms.
How to Prevent an Ear Infection

While not all ear infections can be prevented, there are several measures you can take to reduce the risk (4):
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands regularly, especially before touching your face or ears, to reduce the spread of bacteria and viruses.
- Avoid Smoking or Exposure to Secondhand Smoke: Tobacco smoke can irritate the respiratory system and increase the risk of ear infections.
- Keep Your Ears Dry: Avoid swimming in dirty or contaminated water, and dry your ears thoroughly after swimming or showering. Excess moisture can create a favorable environment for bacteria to grow.
- Avoid Inserting Objects into Your Ears: Using cotton swabs or other objects to clean your ears can push wax deeper into the ear canal and increase the risk of infection.
- Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations: Certain vaccinations, such as the pneumococcal vaccine, can help protect against bacterial infections that can cause ear infections.
- Address Allergies and Sinus Problems: Allergies and sinus conditions can block the Eustachian tubes and increase the likelihood of developing ear infections. Consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options.
The Bottom Line

Ear infections can be painful and disruptive, but recognizing the signs and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing them. If you experience any symptoms of an ear infection, it is vital to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. By practicing good hygiene, keeping your ears dry, and addressing any underlying conditions, you can significantly lower the chances of experiencing an ear infection.
Read More: A Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Could Be Warning You With These 9 Signals
Sources
- “Ear infection (middle ear).” Mayo Clinic
- “Otitis media.” NCBI. Anne G. M. Schilder, Tasnee Chonmaitree,2 Allan W. Cripps, Richard M. Rosenfeld,4 Margaretha L. Casselbrant, Mark P. Haggard, and Roderick P. Venekamp.2016.
- “Ear infections.” NHS
- “Preventing and Treating Ear Infections.” CDC

