Heart failure is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. While heart failure can be managed with the right medical care and lifestyle changes, understanding and identifying the risk factors that contribute to this condition is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Here are eight key risk factors of heart failure to be aware of.
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease is one of the leading causes of heart failure. CAD occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of cholesterol and fatty deposits, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This restricted blood flow can lead to chest pain (angina) or even a heart attack, which can damage the heart muscle and lead to heart failure over time.1
Read More: Signs On Your Face and Head That Could Indicate Heart Trouble
2. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
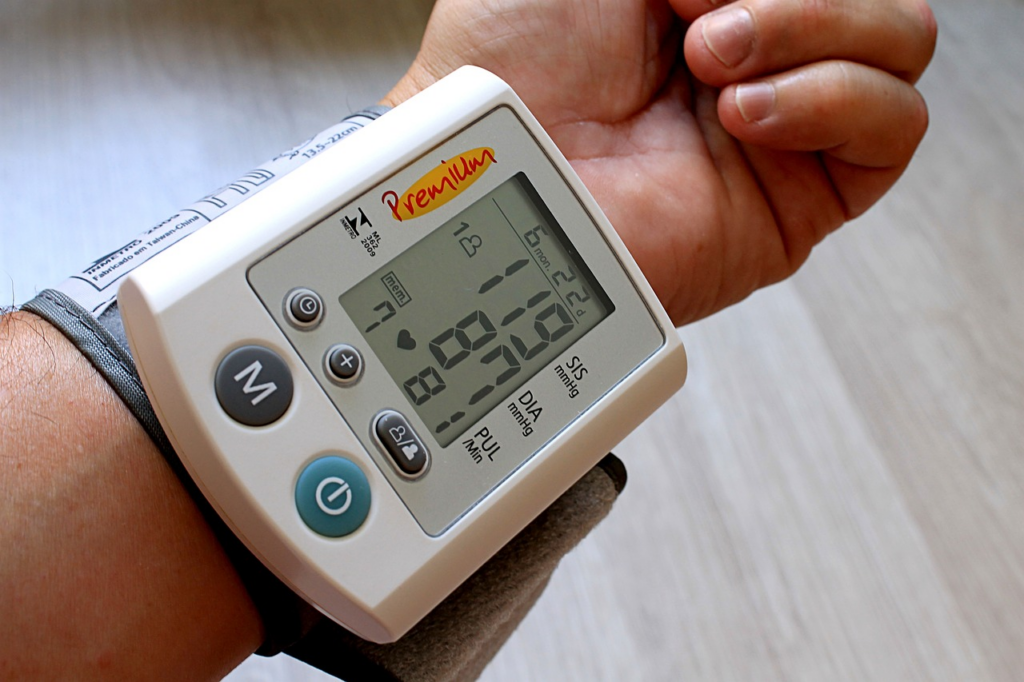
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is another significant risk factor for heart failure. When blood pressure is elevated, the heart has to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. Over time, this extra workload can cause the heart muscles to thicken and become less efficient, ultimately leading to heart failure. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication is essential to reducing this risk.
3. Type 2 Diabetes
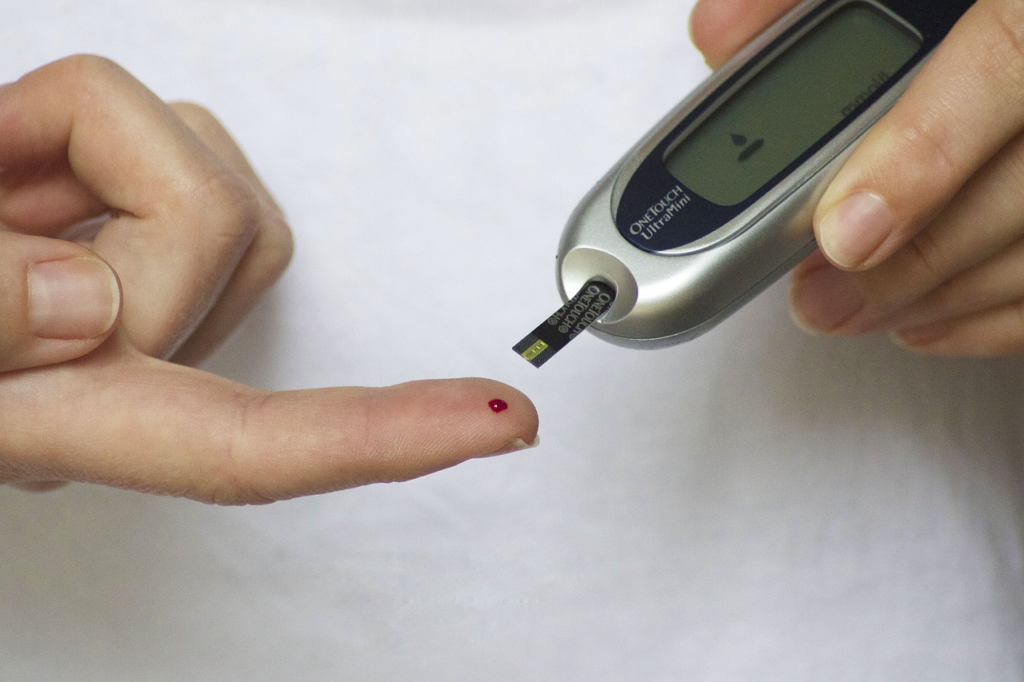
People with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart failure due to the associated complications, such as high blood pressure and atherosclerosis. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and the heart muscle, making it more difficult for the heart to function properly. Controlling blood sugar levels is a critical step in preventing heart failure in individuals with diabetes.2
4. Obesity
Obesity is a major risk factor for heart failure, particularly because it often leads to other conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Excess body weight increases the strain on the heart, forcing it to work harder to pump blood. Losing weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of heart failure⁴.
5. Smoking

Smoking is a well-known risk factor for a variety of cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to conditions such as atherosclerosis and hypertension. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to lower the risk of heart failure and improve overall heart health.
Read More: The ring that lets you feel your partner’s heartbeat from anywhere in the world in real time
6. Alcohol and Drug Abuse
Excessive alcohol consumption and drug abuse can weaken the heart muscle and lead to a condition known as cardiomyopathy, which is a direct precursor to heart failure. Chronic alcohol abuse, in particular, is associated with a higher risk of developing heart failure. Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding illicit drugs are crucial steps in maintaining heart health.
7. Family History of Heart Failure

A family history of heart failure or other cardiovascular diseases can increase your risk of developing the condition. Genetic factors may predispose individuals to heart failure, making it important to be aware of your family’s medical history. If heart failure runs in your family, regular check-ups and proactive management of other risk factors are essential.
8. Age

As people age, the risk of heart failure increases. The heart naturally weakens and stiffens over time, making it more susceptible to failure. Individuals over the age of 65 are at a particularly high risk, especially if they have other underlying conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease. Regular medical screenings and a heart-healthy lifestyle can help mitigate the impact of aging on heart health.
Conclusion

Understanding the factors of heart failure is the first step toward prevention and early intervention. By managing these risk factors—whether through lifestyle changes, medication, or regular medical care—you can reduce your chances of developing heart failure and lead a healthier, more active life. If you are concerned about your risk, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss appropriate measures tailored to your specific needs.
Read More: 13 Health Benefits of Cherries (Sleep, Heart Health, and More)

